BACKGROUND
One of the most extensively studied factors related to aggression among children and adolescents is hostile attribution of intent, also known as hostile attribution bias (de Castro et al., 2002; Verhoef et al., 2019). Hostile attributions refer to individuals’ tendency to interpret others’ ambiguous behavior as intentionally hostile, harmful, or malicious, even when there may be alternative explanations (Smeijers, 2023; Verhoef et al., 2019). Children with a hostile attributional bias perceive others’ actions or intentions negatively, assuming they deliberately try to harm or offend someone (Verhoef et al., 2019). They are susceptible to potential threats or conflicts, just like vulnerable narcissists. Individuals characterized by this type of narcissism have elevated narcissistic vulnerability and antagonism levels (Miller et al., 2021). They “assume the worst” and remain prevention-focused and vigilant to potential danger (Hansen-Brown & Freis, 2021).
Previous research has shown that family factors, such as attachment bonds, parents’ attributional style, and parenting practices, are essential for the development of both narcissistic traits and a hostile attributional style (Dodge, 2006; Horton, 2011; Miller et al., 2011; Xu et al., 2024). However, to our knowledge, no study has linked two maladaptive parenting rearing behaviors to the tendency to make hostile attributions and factors that constitute vulnerable narcissism in adolescents. Meanwhile, exploring such relationships seems important, both from a theoretical and practical point of view – it will provide a better understanding of how hostile attributions arise and operate, and may show important elements in the treatment of cognitive distortions potentially leading to aggression among adolescents. Hence, our research aimed to examine whether parental rejection and overprotection (Arrindell et al., 1999; Koutra et al., 2023) are related to the level of hostile attributions manifested by teenagers. Moreover, knowing that a hostile attribution bias is associated with vulnerable narcissism (Hansen-Brown & Freis, 2021; Miller et al., 2011), we aimed to investigate whether narcissistic vulnerability and antagonism could mediate the relationship between maladaptive parenting practices perceived by adolescents and hostile attributions.
PARENTAL REARING PRACTICES AND HOSTILE ATTRIBUTIONS
Parental rearing practices perceived by children can be assessed on at least three scales: emotional warmth (care), rejection (care), and overprotection (control) (Muris et al., 2003). Emotional warmth characterizes positive parenting and indicates that parents are perceived as accepting and supportive (Arrindel et al., 1999; Poraj-Weder & Woźniak-Prus, 2020). The other two dimensions relate to maladaptive practices. Rejection indicates that parents are viewed as critical, hostile, and prone to frequent punishment, while overprotection indicates that parents are perceived as intrusive and controlling, hindering the child’s development of independence and autonomy (Arrindel et al., 1999; Poraj-Weder & Woźniak-Prus, 2020). Maladaptive rearing behaviors are associated with adverse outcomes for children, such as social incompetence, interpersonal problems, low self-esteem, social isolation, loneliness, and higher internalizing-externalizing problems (Pinquart, 2017). Moreover, it seems that parental rejection and overprotection can lead to developing a hostile attributional style.
Dodge (2006) proposed that hostile attributional style stems from a failure to develop the ability to make benign attributions. This failure arises from a combination of individual differences and life experiences involving a lack of secure attachment patterns. Previous research has shown a significant association between insecure attachment and perceived parental rearing practices (Li et al., 2023; Muris et al., 2000, 2003; Roelofs et al., 2006). Parental rejection is related to avoidant attachment style. In turn, anxious rearing, close to overprotection, is linked to an ambivalent attachment style (Muris et al., 2000). Following Dodge’s model (2006), various unfavorable factors appearing in the child’s life accumulate and interact, forming hostile schemas stored in the memory. During social interactions, individuals with hostile schemas tend to interpret others’ intentions as threatening and hostile (Crick & Dodge, 1994; Dodge, 2006; Smeijers, 2023). One environmental factor that encourages the formation of hostile schemas and, consequently, attributional style may be an experience of adverse parenting (Lee et al., 2019). In turn, an increasingly mentioned individual factor is vulnerable narcissism (Hansen-Brown & Freis, 2021; Miller et al., 2011).
PARENTAL REARING PRACTICES AND NARCISSISM
Concepts about the formation of narcissism often involve experiences with parents (Horton, 2011). For example, Kernberg (1986) claimed that narcissism develops in children due to rejecting, strict, and emotionally cold parenting. In contrast, Millon (1990) suggested that narcissism develops due to a parent’s excessive focus on the child. More recent theories integrating psychodynamic and social-cognitive approaches also pay attention to the quality of parenting (Drozek & Unruh, 2020). However, they indicate that the ethology of narcissism can differ depending on its type (Horton, 2011).
Paul Wink suggested that narcissism is a multidimensional construct and defined two faces of narcissism (Wink, 1991): grandiose-exhibitory and vulnerable-sensitive. Grandiose narcissism is related to extraversion, higher self-esteem, sociability, and entitlement. In turn, vulnerable narcissism is associated with neuroticism, egocentrism, low or unstable self-esteem, and distrust of others (Miller et al., 2021). Vulnerable narcissism but not grandiose is associated with the tendency to make hostile attribution (Bodecka-Zych et al., 2022a; Hansen-Brown & Freis, 2021), which can be understood, on the one hand, as a projection of internalized hostility and, on the other, as a defensive strategy to respond quickly to a constantly anticipated threat.
However, the latest research indicates that narcissism can be conceptualized through three facets: agentic, antagonistic, and neurotic (Miller et al., 2021; Rogoza et al., 2022). Antagonism is common to grandiose and vulnerable narcissism and hides cynicism, arrogance, callousness, and a sense of entitlement. Agentic extraversion is unique to grandiose narcissism and related to assertiveness, leadership, and high self-esteem. In turn, narcissistic neuroticism or vulnerability is characteristic of vulnerable narcissism and associated with emotional dysregulation, experience of shame, and contingent self-esteem (Miller et al., 2021). The three-factor model of narcissism is a relatively new concept. Therefore, little is known about the factors that promote the development of particular facets.
CURRENT STUDY
Hostile attributions of intent are associated with both externalizing and internalizing problems in children and adolescents (Crick & Dodge, 1994). Most widely studied are their links to violent behaviors (Verhoef et al., 2019). Theoretical concepts indicate that maladaptive parenting practices can lead to developing a hostile attributional style, but few empirical studies exist on the subject. There is also a gap in research on parenting behaviors linked to developing facets of narcissism. Therefore, in the current study, we examined whether maladaptive parental practices (rejection by mother and father; overprotection by mother and father) and facets of vulnerable narcissism (narcissistic vulnerability and antagonism) are related to adolescents’ hostile attributions. Moreover, given the well-known connection between vulnerable but not grandiose narcissism and a hostile attributional style (Hansen-Brown & Freis, 2021), we hypothesized that the relationship between parental rearing behaviors (perceived by adolescents) and hostile attributions is mediated by narcissistic vulnerability and antagonism.
PARTICIPANTS AND PROCEDURE
PARTICIPANTS
The study included 268 teenagers, 134 females, 121 males, and 13 individuals identified as ‘other’ for gender. The participants were aged between 12 and 17 years (M = 13.34, SD = 0.70). The study was conducted in Poland, in four public schools located in different parts of the country. Half of the sampled teenagers (50%) declared that they lived in a town (less than 100,000 residents). The rest were mainly from rural areas (47.8%), while a small proportion of respondents (1.9%) lived in a large city (more than 100,000 residents). Most of the participants came from a family where the parents had an average (31.7% of mothers and 41% of fathers) or high (56.7% of mothers and 41% of fathers) education level and had one (59%) or two siblings (21.3%).
PROCEDURE
Before the survey, consent was obtained from the school principals and legal guardians of the participating students. The adolescents were also asked for their consent and informed that they could discontinue at any time and that their responses would be anonymous. The survey was group-based. Students filled out individual questionnaires, but the whole procedure took place in the classroom. The teachers were asked to ensure calm and confidentiality. The procedure was as follows: the teacher displayed a QR code on the screen redirecting participants to an individualized, anonymized survey designed in Qualtrics software (Copyright 2020, https://www.qualtrics.com) or handed out paper questionnaires. The students individually answered the questions, starting with demographic data and then filling out the questionnaires, the order of which was rotated.
MEASURES
Parental rearing behaviors. The My Childhood Memories questionnaire (s-EMBU) was used to assess parental rearing behaviors. This questionnaire is a Polish adaptation (Poraj-Weder & Woźniak-Prus, 2020) of the Egna Minnen Beträffande Uppfostran tool developed by Arrindell et al. (1999). The tool has been adapted to measure parental parenting behavior as perceived by their children.
It consists of two parts, one focusing on the mother’s parental practices (23 items) and the other on the father’s parental practices (23 items). The s-EMBU captures parental behavior through three dimensions: emotional warmth, rejection, and overprotection (Arrindell et al., 1999). The Cronbach’s α reliabilities of all scales in the current study were acceptable: for emotional warmth of the mother: .84; for emotional warmth of the father: .90; for rejection by the mother: .84; for rejection by the father: .82; for overprotection by the mother: .76; for overprotection by the father: .73.
Narcissistic vulnerability and antagonism. To assess the levels of narcissism in teenagers, we employed the Polish version of the Adjective Narcissism Scales (Rogoza et al., 2020). This instrument comprises 12 adjectives that capture various characteristics of an individual. The adjectives correspond to three facets of narcissism (Rogoza et al., 2022), which form three separate scales: the Narcissistic Vulnerability Scale (NVS), the Narcissistic Antagonism Scale (NAS), and the Narcissistic Grandiosity Scale (NGS). Participants were instructed to read each adjective and indicate the extent to which they felt that each adjective described them. The Cronbach’s α reliabilities of all the scales yielded acceptable values: for narcissistic vulnerability: .84; for narcissistic antagonism: .77; for narcissistic grandiosity: .87.
Hostile attributions. To measure teenagers’ levels of hostile attributions, we used a self-developed tool, created for a previous study (Bodecka-Zych et al., 2022b). At first, we presented three brief narratives depicting fictional situations where the underlying reasons for the behaviors described are unclear (see Supplementary materials). The scenarios represented typical situations used in hostile attribution research (Combs et al., 2007; Crick, 1995). After each scenario, the young people answered three questions measuring hostile attribution subfactors: intentionality, blame ascription, and angry feelings. In the current study, the Cronbach’s α reliabilities of responses regarding each scenario were, respectively: .65, .70, and .81.
Afterward, the teenagers were instructed to provide two instances where they experienced negative emotions due to someone’s behavior towards them, such as actions from a peer. This research method was previously employed by Quigley and Tedeschi (1996), and the current study used the same set of instructions (see Supplementary materials). Following the description of each situation, participants again responded to three questions evaluating intentionality, blame, and feelings of anger (the reliability of responses regarding their own scenarios was, respectively: .90 and .90). The rate of hostile attributions was determined by averaging the responses for all three questions across five situations. The Cronbach’s α reliability of the whole tool was good, at .82.
ANALYTIC STRATEGY
In our study, we took the threshold of p < .05 to infer statistical significance. Before proceeding with the mediation analysis, we checked regression-based model assumptions of variable distributions’ normality (skewness and kurtosis check) and performed a residual autocorrelation test (the Durbin-Watson statistic), homoskedasticity tests (Breusch-Pagan and Koenker tests conducted with HeteroskedasticityV3 macro for SPSS; Daryanto, 2020), and a multicollinearity test (variance inflation factor – VIF).
The main hypotheses were tested with the PROCESS 4.2 macro for SPSS and Windows. The macro performs ordinary least squares regression analysis to test various moderation and mediation models. The mediation model number 4 (numeration according to the PROCESS documentation, which also contains the syntax, Hayes, 2018). When performing the mediation analysis, we used the bootstrap sample size of N = 5000, which is also the default in the macro.
RESULTS
The correlation analysis suggested that all of the variables of interest were significantly and positively correlated. The prerequisites for mediation analysis were thus fulfilled. For exploratory purposes, we include the full correlation and descriptive statistics (mean, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis) table, including all measured types of parental attitudes and narcissism in Supplementary materials.
Next, we tested for the potential confounding effect of gender. We found that gender was not related significantly to the dependent variable (hostile attributions). Out of the variables of interest for the current models, it was only weakly and significantly related to narcissistic vulnerability, with girls being prone to display it more. In light of this evidence, we decided not to include this variable in the final model.
Assumptions for mediation analysis were fulfilled, given that the distribution of all variables of interest was close to normal, and that skewness ranged from –0.51 to 1.48 and kurtosis from –1.02 to 2.10 (falling within the ranges proposed by Byrne, 2010, and Hair et al., 2010). Moreover, the autocorrelation of residuals was not present, given that the Durbin-Watson statistic was close to the value of 2 in all cases (ranging from 1.82 to 1.86 across the four models). The Breusch-Pagan and Koenker’s tests were insignificant for all models (p > .05), suggesting no heteroskedasticity. Finally, no multicollinearity was detected, given that VIF scores ranged from 1.23 to 1.65 across all four models. Therefore, we proceeded with the mediation analysis.
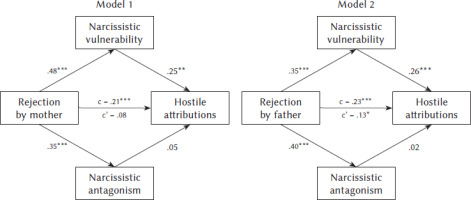
For model 1, before including mediators in the model, the total effect of rejection by the mother on hostile attributions was significant and positive, B = .21; 95% CI [.10; .33], and accounted for 4.6% of the variance in hostile attributions. Rejection by the mother also significantly and positively related to narcissistic vulnerability, B = .48; 95% CI [.37; .59], accounting for 23.0% of its variance, and to narcissistic antagonism, B = .35; 95% CI [.23; .46], accounting for 12.1% of its variance. In the full model taking into account all these predictors, only narcissistic vulnerability related significantly and positively to hostile attributions, B = .25; 95% CI [.10; .40], whereas rejection by the mother, B = .08; 95% CI [–.05; .21], and narcissistic antagonism, B = .05; 95% CI [–.09; .19], were unrelated to hostile attributions. The indirect effect of rejection by the mother mediated by narcissistic vulnerability on hostile attributions was statistically significant, B = .12, 95% CI [.04; .22]. The whole model accounted for 10.5% of the variance in hostile attributions.
For model 2, before including mediators in the model, the total effect of rejection by the father on hostile attributions was significant and positive, B = .23; 95% CI [.11; .35], and accounted for 5.3% of the variance in hostile attributions. Rejection by the father also significantly and positively related to narcissistic vulnerability, B = .35; 95% CI [.24; .46], accounting for 12.3% of its variance, and to narcissistic antagonism, B = .40; 95% CI [.29; .51], accounting for 15.9% of its variance. In the full model taking into account all these predictors, rejection by the father, B = .13; 95% CI [.01; .26] and narcissistic vulnerability, B = .26; 95% CI [.12; .39], related significantly and positively to hostile attributions, whereas narcissistic antagonism, B = .02; 95% CI [–.12; .16], was unrelated to hostile attributions. The indirect effect of rejection by the father mediated by narcissistic vulnerability on hostile attributions was statistically significant, B = .09, 95% CI [.03; .17]. The whole model accounted for 11.5% of the variance in hostile attributions.
We present the results of the analysis for models 1 and 2 in Table 1 and Figure 1.
Table 1
Testing the mediation effect of narcissistic vulnerability and narcissistic antagonism in the relationship between rejection by mother (Model 1) or father (Model 2) and hostile attributions
Figure 1
Graphical overview of the models testing the mediating effects of narcissistic vulnerability and antagonism in the relationship between rejection by mother (Model 1), rejection by father (Model 2) and hostile attributions
Note. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001.
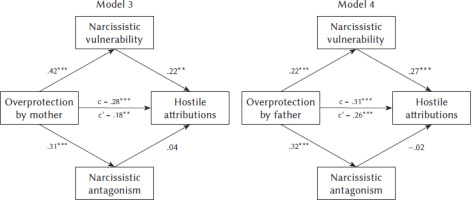
For model 3, before including mediators in the model, the total effect of overprotection by the mother on hostile attributions was significant and positive, B = .28; 95% CI [.17; .40], and accounted for 8.0% of the variance in hostile attributions. Overprotection by the mother also significantly and positively related to narcissistic vulnerability, B = .42; 95% CI [.31; .53], accounting for 17.6% of its variance, and to narcissistic antagonism, B = .31; 95% CI [.20; .43], accounting for 9.8% of its variance. In the full model taking into account all these predictors, overprotection by the mother, B = .18; 95% CI [.05; .31] and narcissistic vulnerability, B =. 22; 95% CI [.07; .36], related significantly and positively to hostile attributions, whereas narcissistic antagonism, B = .04; 95% CI [–.10; .17], was unrelated to hostile attributions. The indirect effect of overprotection by the mother mediated by narcissistic vulnerability on hostile attributions was statistically significant, B = .09, 95% CI [.02; .18]. The whole model accounted for 12.7% of the variance in hostile attributions.
For model 4, before including mediators in the model, the total effect of overprotection by the father on hostile attributions was significant and positive, B = .31; 95% CI [.20; .43], and accounted for 9.7% of the variance in hostile attributions. Overprotection by the father also significantly and positively related to narcissistic vulnerability, B = .22; 95% CI [.10; .33], accounting for 4.7% of its variance, and to narcissistic antagonism, B = .32; 95% CI [.20; .43], accounting for 10.0% of its variance. In the full model taking into account all these predictors, overprotection by the father, B = .26; 95% CI [.14; .38], and narcissistic vulnerability, B = .27; 95% CI [.13; .40], related significantly and positively to hostile attributions, whereas narcissistic antagonism, B = –.02; 95% CI [–.15; .12], was unrelated to hostile attributions. The indirect effect of overprotection by the father mediated by narcissistic vulnerability on hostile attributions was statistically significant, B = .06, 95% CI [.02; .12]. The whole model accounted for 16.1% of the variance in hostile attributions.
We present the results of the analysis for models 3 and 4 in Table 2 and Figure 2.
Table 2
Testing the mediation effect of narcissistic vulnerability and narcissistic antagonism in the relationship between overprotection by mother (Model 3) or father (Model 4) and hostile attributions
DISCUSSION
The aim of the current study was to evaluate whether maladaptive parental practices and narcissistic vulnerability and antagonism are related to adolescents’ hostile attributions. All the variables of interest were positively correlated. Thus we could conduct mediation analyses. We hypothesized that the relationships between parental rearing behaviors and hostile attributions of teenage children are mediated by narcissistic vulnerability and antagonism. The results showed that narcissistic vulnerability, but not antagonism, was an important mediator between maladaptive parenting practices and adolescents’ hostile attributional style.
In more detail, the results showed that both rejection by the mother and rejection by the father were significant predictors of teenagers’ hostile attributions. Moreover, we found that parental rejection was positively related to children’s narcissistic vulnerability and antagonism. However, in the model regarding rejection by the mother, in which all these predictors were taken into account, only narcissistic vulnerability remained positively and significantly related to hostile attributions. In the model regarding rejection by the father, both rejection and narcissistic vulnerability remained significant. Narcissistic vulnerability fully mediates the relationship between rejection by the mother and adolescents’ hostile attributions and partially mediated the relationship between father rejection and hostile attributional style manifested by the teenage child.
In the case of parental overprotection, the results were similar. Overprotection displayed by either the mother or the father was a significant predictor of adolescents’ hostile attributions, narcissistic vulnerability, and antagonism. Moreover, the relationship between the mother and father’s overprotection and teenagers’ hostile attributions was found to be partially mediated by narcissistic vulnerability but not by narcissistic antagonism. Thus, rejection by parents (especially by the mother) and their overprotection could lead to the development of narcissistic vulnerability, which in turn fosters the making of hostile attributions. Our findings are in line with previous research indicating that parental rejection and overprotection are significantly related to anxiety, anger and hostility, emotion dysregulation, and shame (Mills, 2005; Muris et al., 2004). However, the study sheds new light on the role of narcissistic vulnerability in the emergence of adolescents’ hostile attributions.
In clinical terms, narcissistic vulnerability could be understood as an injury. It is the most sensitive aspect of the narcissistic self, which is protected by all available means. This part of the personality hides anger, helplessness, and emptiness (Pincus et al., 2009). Parental rejection or overprotection could be the reason for this hurt. According to psychodynamic concepts, when a child experiences inadequate parental care, they attribute the blame to themselves: “There is something wrong with me if mom/dad rejects me or still protects me”. Empirical studies confirmed these assumptions and indicated that both maladaptive parental practices and narcissistic vulnerability are positively related to self-conscious emotions such as shame (Meesters et al., 2017).
Shame is acknowledged as one of the most damaging emotions, resulting from an internal attribution of an adverse event, and is about a sense of the self as inferior, undesirable, defective, or powerless (Tracy et al., 2011). Shame resulting from parental rejection could be a way to self-regulate by disengaging and be caused by a sense of being insignificant. In turn, shame resulting from overprotection could be caused by a sense of uncontrollability and inefficacy (Mills, 2005). Narcissistic vulnerability, linked with shame and related to neuroticism (Miller et al., 2021), can make the world and other people appear dangerous. If a young person feels they must constantly protect themselves from humiliation, the best strategy is to assume the worst. That is, to make hostile attributions in ambivalent situations and sometimes even in situations without cues of hostile intentions (Hansen-Brown & Freis, 2021).
LIMITATIONS AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
Survey-based research has implications that stem from its inherent limitations. One of these is the issue of relying on participants to remain honest. Adolescents are known to be particularly sensitive to factors related to social approval, which may influence the honesty of their answers. The survey was conducted in class, in the presence of classmates and the teacher. As a result, some students, particularly those sensitive to social approval, may have been afraid to provide certain answers or may have given responses they believed would be liked by their peers, such as funny or inconsistent answers. Moreover, parental behaviors as perceived by teenagers may differ from the actual behaviors exhibited by parents. In addition, the correlational nature of our study precludes conclusions about the cause and effect of the relationship between hostility, two types of narcissism, and parental rejection and overprotection.
Finally, the study was carried out in a normative group. It would be valuable to verify the results in a clinical group, for example, among adolescents with problems in interpersonal relationships or displaying aggressive behavior. Notably, a previous study on narcissism and hostile attributions, conducted among adults and taking into account the socio-relational context, found subtle differences between the normative and clinical samples (Bodecka-Zych et al., 2022a). For our model, we assume that the relationships between variables would be stronger for the clinical group; however, this requires empirical verification.
Despite such limitations, our study may contribute to a better understanding of the mechanisms of developing a hostile attributional style. We believe that drawing attention to narcissistic vulnerability will be helpful in therapeutic work with young people who tend to make hostile attributions. Given the results of the current study, it seems important to work not only on modifying cognitive distortions that promote hostile attributions (Hansen-Brown & Freis, 2021), but also on enhancing strengths and fragile self-esteem to reduce insecurity and shame. Moreover, the current study highlights the role of the father’s parenting behaviors, not just the mother’s, which appear more often in previous research. The father plays a very important role in the child’s life (e.g. Gwiazdowska-Stańczak et al., 2021). Recognizing the significance of the father’s rearing behaviors can also contribute to more effective work with adolescents and the family system. In the case of younger adolescents, it seems important to include parents – both the mother and father – in therapeutic work and support them in building a warm relationship with their adolescent child.
Supplementary materials are available on the journal’s website.